POLAR ENCODING
POLAR ENCODING
Polar encoding uses
two levels ( positive and negative)
of amplitude.
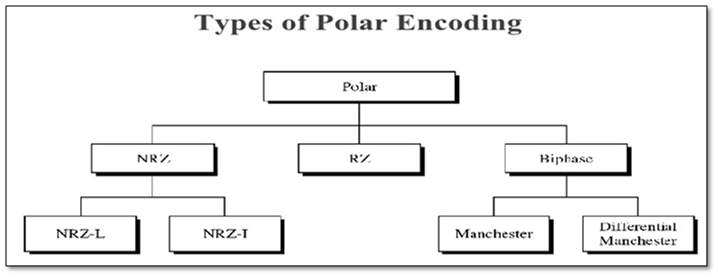
The polar encoding is catagorise into 3 types :-
·
NRZ(non return
to zero)
·
RZ(return to
zero)
·
Biphase
Non Return To
Zero (NRZ)-
In NRZ encoding , The
level of the signal is always either
positive of negative .
The NRZ
encoding includes two methods :-
·
Non Return To Zero ,Level (NRZ-L)
·
Non Return To Zero ,Invert (NRZ-I)
NRZ-L :-
In NRZ-L encodingthe level of the signal depends on the type
of bit it represents.
§ A positive
voltage means the bit is 0 , and a negative voltage means the bit is 1 .
§ Thus the level
of the signal is dependent upon the state of the bit.
NRZ-I :-
In NRZ-I , on inversion of voltage level represents a 1 bit.
A 0 bit is represented by no change .
NRZ-I is superior to NRZ-L due to the synchronization
provided by signal change each time a 1 bit is encountered.
NOTE- In NRZ-I
the signal is inverted if a binary 1 is encountered.
For Example – In NRZ-L , The binary 0s is represented by positive voltage and binary 1s is represented
by negative voltage.
In NRZ-I , The binary 0s is represented by no change &
Binary 1 is represented by inversion of the voltage level.
Fig. showing
NRZ-L & NRZ-I encoding
Return To Zero (RZ) –
Return to zero encoding uses Three values :
§ positive
§ negative
§ zero
·
In RZ the signal changes not between bits but during each
bits.
·
In RZ the binary 0s is
reprented by negative-to-zero and
the binary 1s is represented by positive-to-zero.
Fig. showing RZ
encoding
Biphase Encoding –
The Biphase encoding is the best existing
solution to the problem of synchronization.
In this method ,
The signal changes at the middle of the bit intervel but doses not return to
zero , Instead it continues to the opposite pole.
Biphase
encoding is classified into 2 types :-
·
Manchester
Encoding
·
Differential
Menchester Encoding
Manchester
Encoding :-
§ In Manchester
encoding , The transition at the middle of the bit is used for both synchronization and bit reprentation.
§ In Manchester
encoding , The binary 0s is represented by a positive-to-negative transition and The binary 1s is represented by
negative-to-positive transition.
Fig. showing
manchester encoding
Differential
Manchester Encoding –
§ In Differential
Manchester , The inversion at the middle of bit interval is used for synchronization.
§ A transition
means Binary 0 & no transition means Binary 1.
§ Differential
Manchester requires two signal changes to represent binary 0 , But only one to
represent binary 1.
Fig. showing Differential manchester
Bipolar Encoding
–
Bipolar encoding uses three voltage levels :-
·
positive
·
negative
·
zero
§ In bipolar
encoding the binary 0s is represented by zero level And Binary 1s is
represented by alternating positive and
negative voltage.
§ If the first 1
bit is represented by the positive amplitude , The second will be represented
by the negative amplitude , The third by the positive amplitude & so on…
The bipolar encoding is classified into 3 types :-
·
AMI(Bipolar
Alternate Mark Inversion)
·
B8ZS(Bipolar
8-Zero Substitution)
·
HBD-3(High
Density Bipolar 3)
Bipolar
Alternate Mark Inversion(AMI) –
§ Bipolar
Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) is the simplest type of bipolar encoding.
§ The AMI means alternate 1 inversion . In AMI
encoding , The binary 0s is represented by neutral , zero voltage & Binary
1s is reprented by alternating positive
and negative voltage.
Fig.
showing Bipolar AMI Encoding





Comments
Post a Comment